Collections in Kotlin: Explanation of Lists, Sets and Maps
Let's get started.
Collections are one of the most important aspects of programmin. We use them to group, store and manipulate data efficiently. Kotlin, provides a powerful and type-safe collection framework that’s both easy to use and concise.
Kotlin’s Collection Framework Overview
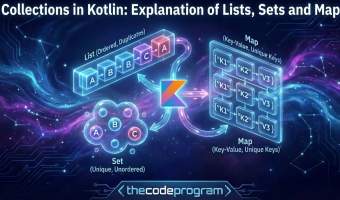
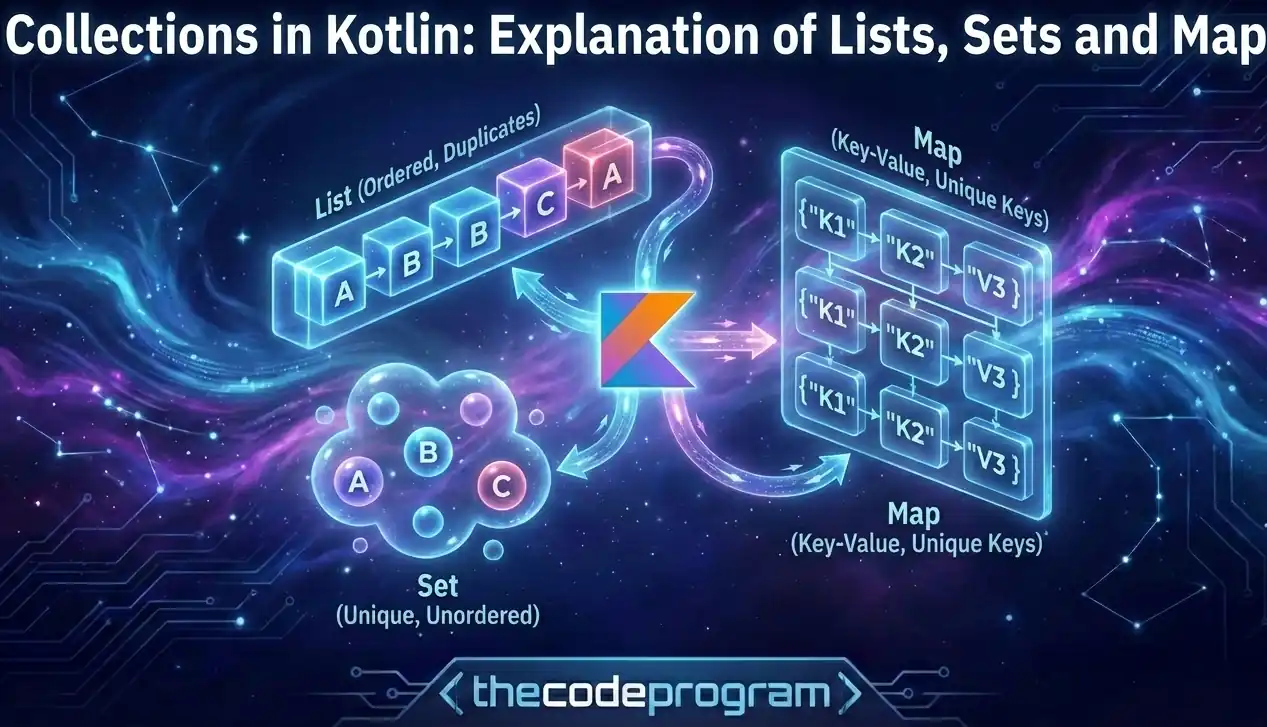
Kotlin standard library provides three main types of collections: Each of these comes in two flavors:This separation allows Kotlin to promote immutability by default, while still allowing mutability when explicitly needed.
Lists in Kotlin
Read-only Lists
A read-only list (List
val fruits = listOf("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry")
println(fruits[0]) // Apple
println(fruits.size) // 3
println("Banana" in fruits) // true
Mutable Lists
When you need to change the content you need to use a MutableList:
val numbers = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
numbers.add(4)
numbers.remove(1)
println(numbers) // [2, 3, 4]
Sets in Kotlin
Set is a collection of unique elements. Duplicates are automatically filtered out according to data structure of Set. We can create an immutable set collection with setOf initiatior method.
val colors = setOf("Red", "Green", "Blue", "Red")
println(colors) // [Red, Green, Blue]
To create a modifiable set:
val mutableColors = mutableSetOf("Cyan", "Magenta")
mutableColors.add("Yellow")
mutableColors.remove("Cyan")
println(mutableColors) // [Magenta, Yellow]
Maps in Kotlin
Map
val countryCapitals = mapOf(
"France" to "Paris",
"Japan" to "Tokyo",
"India" to "New Delhi"
)
println(countryCapitals["Japan"]) // Tokyo
val mutableMap = mutableMapOf(
"A" to 1,
"B" to 2
)
mutableMap["C"] = 3 // add a new key
mutableMap.remove("A")
println(mutableMap) // {B=2, C=3}
Collection Operations
Kotlin collections has built-in functional-style operations to iterate and process the data in the collection. Now lets take a look at these operations.
Filtering
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
val even = numbers.filter { it % 2 == 0 }
println(even) // [2, 4, 6]
Mapping
val squared = numbers.map { it * it }
println(squared) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
Aggregation
val sum = numbers.sum()
val average = numbers.average()
println("Sum: $sum, Average: $average")
Grouping and Sorting
val words = listOf("apple", "ant", "banana", "berry", "cherry")
val grouped = words.groupBy { it.first() }
println(grouped)
/* Prints:
{
a=[apple, ant],
b=[banana, berry],
c=[cherry]
}
*/
Use mutable variants only when you must modify collections frequently or require performance optimization for large mutable datasets.
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3)
val set = list.toSet() // Converts List → Set
val map = list.associateWith { it * it } // List → Map (1→1, 2→4, 3→9)
When you’re managing simple lists or complex maps, Kotlin offers useful and efficient methods and type-safety that lead to clean, maintainable code.
That is all.
Burak Hamdi TUFAN